What are Masternodes and Why do People Run them?
Masternodes are increasing in popularity across the cryptocurrency sector. There are now over 400 blockchain-based projects that allow members of their community to run masternodes on their blockchain. In addition, search volumes for the term masternode have been at a consistently higher rate this year versus last year (but still much lower compared to January).

What are masternodes?
Masternodes are a type of node that performs specialized functions on a blockchain. They are servers that are established by community members once they have fulfilled certain criteria. Masternodes are also known as bonded validator systems.
Masternodes first came into existence through Dash (DASH). The privacy-centric altcoin introduced the concept in order to allow for instant transactions as well as facilitate its PrivateSend function which enables private transactions. As an added incentive, those running masternodes were provided with the advantage of participating in the governance model of the community. This is converse to normal nodes who are not able to vote.
To run a masternode, one will need to put up a significant amount of tokens. This is because masternodes operate similarly to the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. The amount required to set up a masternode varies from blockchain to blockchain. While bonded validator systems require a stake of the token in question in order to function, they should not be confused with proof-of-stake systems. Different blockchains with varied consensus mechanisms can employ masternodes regardless of what method they use to achieve consensus.
As a result of their continued success in the Dash ecosystem, a number of blockchain projects have implemented the system. However, different blockchain projects are utilizing masternodes to facilitate a number of varied features within their networks. Similar to Dash, PIVX, a privacy-focused decentralized open source cryptocurrency, uses masternodes to facilitate private transactions. However, Syscoin, a blockchain platform and cryptocurrency, uses them to power a decentralized marketplace. Additionally, Exscudo, a gateway between the traditional financial system and the cryptocurrency market, has a decentralized exchange powered by a network of bonded validators.
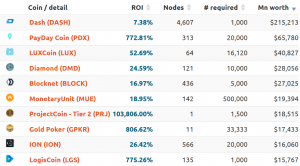
You can find the list of masternodes, information about their worth and annual return on investment here.
Why do people run masternodes?
Running a masternode requires the creator to hold a significant amount of the token in question. For instance, within the Dash network, a masternode operator must hold a minimum of 1,000 DASH (USD 215,029) in their dedicated wallet. If the operator was to move this amount from the wallet, then they would no longer be a masternode nor would they be able to access any of the advantages afforded to masternodes.
This begs the question why people would willingly lock up a significant amount of their crypto in this manner. The answer is simple. Masternodes are entitled to a portion of the block rewards. The percentages vary from blockchain to blockchain, however, this entitles masternode operators to a guaranteed amount every so often. Their portion of the block reward justifies their significant initial investment.
Top 10 most expensive masternodes:
Moreover, running a masternode is considered a smarter way of HODLing, because it puts the tokens that one possess to work and creates a profit for the operator. The Dash community explains this analogy: “Think of a masternode as a savings account with a minimum deposit of 1,000 DASH. A traditional savings account pays interest, and a masternode pays rewards which are very much like interest. In the case of a masternode, the reward (or interest) comes from performing services for the network. Not from lending. The big difference between a traditional savings account and a masternode is that your initial deposit never leaves your possession.”
Pros and cons for the blockchain ecosystem
While people who meet the criteria are able to capitalize on masternodes for profit, these servers also hold advantages for the crypto ecosystem. In addition to allowing a network to introduce more features into its blockchain through the second level of servers, masternodes also help to keep a blockchain secure.
This is because they help networks evade any centralization that may occur as a result of mining pools. While proof-of-work continues to be a popular consensus method, it is not without its challenges. However, the addition of masternodes can help combat this. In many cases, masternode operators are able to accept or reject transactions by guaranteed by miners. This gives them some oversight authority and helps to keep the miners in check. This system of checks and balances results in greater security and stability for the network.
Some argue that the amount would-be masternode operators require in order to begin lends itself to a certain level of centralization. However, it is important to remember that masternode operators are incentivized to stay honest because they want to protect their sizeable investment.
Additionally, while a 51% attack by a masternode operator is theoretically possible, it is very unlikely due to the amount that the attacker would need in order to establish a network of dishonest masternodes. For smaller networks, this probability increases, however, it still requires significant capital.




