Best Deflationary Cryptocurrency Projects to Buy in 2024

Deflationary cryptocurrencies have a total token supply that decreases over the course of time. This means that in theory, the value of the cryptocurrency will increase as the supply is reduced, not least because the token becomes scarcer. In this guide, we analyze the best deflationary cryptocurrency to consider investing in today.
The 10 Best Deflationary Cryptos to Invest in
After countless hours of market research, we found that the 10 best deflationary cryptocurrency assets are those listed below:
- Bitcoin ETF Token – Top deflationary token with a generous staking APY and burn mechanics based on events around the Bitcoin spot ETF approval by the SEC. The presale already raised over $100,000 within just a few days of launch.
- Bitcoin Minetrix – A crypto token set to redefine the Bitcoin mining landscape. Its eco-friendly approach, a simplified Bitcoin cloud mining process, and high-security measures offer a promising avenue for passive income.
- Pikamoon – New play-to-earn metaverse and NFT gaming marketplace. 5% of all $PIKA tokens spent on the NFT marketplace is burned. Pikamoon is offering 15 billion tokens through the ongoing presale.
- Bitcoin – Deflationary cryptocurrency with a cap of just 21 million BTC tokens.
- BNB – Large-cap cryptocurrency with frequent token burns.
- XRP – Interbank payment network that automatically burns transaction fees.
- Cronos – Proof of authority blockchain that backs the Crypto.com ecosystem.
- Shiba Inu – Meme coin and metaverse project with a deflationary supply.
- PancakeSwap – Ongoing burning mechanism reduces the long-term supply of CAKE.
- Polygon – EIP-1559 deployment means that MATIC fees are burned.
Analyzing the Best Deflationary Cryptocurrencies
It goes without saying that investors shouldn’t look to gain exposure to a cryptocurrency just because it is deflationary. On the contrary, in-depth research needs to be conducted into the future potential of the cryptocurrency, from an investment perspective. To help clear the mist, we will now analyze the 10 best deflationary cryptocurrency assets in the market right now.
1. Bitcoin ETF Token – Best Deflationary Token With Up To 25% Token Burn Mechanics And Over 2,000% Staking APY
Bitcoin ETF Token is a token presale built on the Ethereum blockchain designed to reward holders based on events surrounding the Bitcoin spot ETF approval by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). It has one of the best deflationary measures, starting from 5% token burn tax on every transaction and 5% of the total supply burned when certain milestones around the Bitcoin ETF approval are reached. Buy $BTCETF tokens by connecting your MetaMask wallet, or any other Ethereum-based wallet, to the Bitcoin ETF Token presale site. Use ETH, USDT or a card to buy as many tokens as you want. There’s also the option to buy with MATIC and BNB but you won’t be eligible for the staking APY if you purchase $BTCETF with these two crypto coins.  There are 10 presale stages where the price of $BTCETF rises with each stage, starting from $0.0050 per token in the first stage and goes as high as $0.0068 in the last stage. If you scoop up $BTCETF tokens during the first stage and sell them at the same price as the last stage you would earn 36%. No matter during which presale stage you buy, there’s a generous staking APY of over 2,000% in the early stages that will slowly go down as more tokens are staked. If you’re looking to buy $BTCETF tokens anyway, staking them early could be worth it.
There are 10 presale stages where the price of $BTCETF rises with each stage, starting from $0.0050 per token in the first stage and goes as high as $0.0068 in the last stage. If you scoop up $BTCETF tokens during the first stage and sell them at the same price as the last stage you would earn 36%. No matter during which presale stage you buy, there’s a generous staking APY of over 2,000% in the early stages that will slowly go down as more tokens are staked. If you’re looking to buy $BTCETF tokens anyway, staking them early could be worth it. 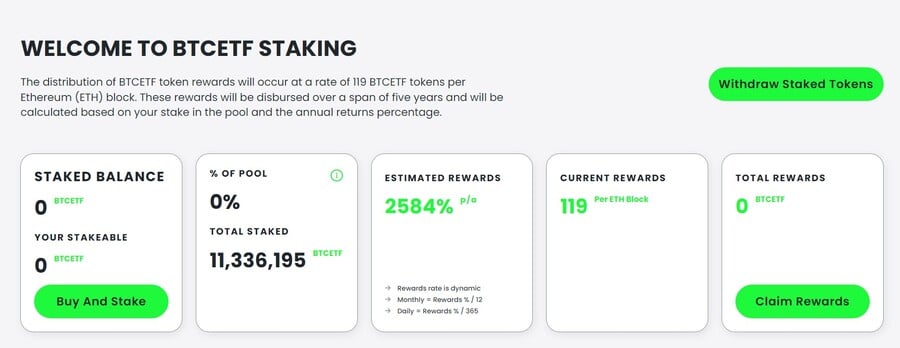 Out of the 2.1 billion total token supply, 25% of it will be forever removed from circulation in 5% increments as event milestones around the spot Bitcoin ETF approval unfold. The milestones that will trigger token burn include:
Out of the 2.1 billion total token supply, 25% of it will be forever removed from circulation in 5% increments as event milestones around the spot Bitcoin ETF approval unfold. The milestones that will trigger token burn include:
- $BTCETF token reaches $100 million trading volume.
- The first Bitcoin ETF is approved.
- The first Bitcoin ETF is launched.
- The total assets under management for all Bitcoin ETFs reaches $1 billion in value.
- Bitcoin reaches a price of over $100,000.
There will also be a 5% token burn tax for every transaction, which will drop to 0% as each of the previous milestones are reached. https://youtu.be/7NhSSPSzmJ4 Follow Bitcoin ETF Token on X and join the Bitcoin ETF Token Telegram channel to get the latest news about the Bitcoin ETF approval and the $BTCETF project. Make sure to read the Whitepaper as well.
| Presale Started | 6 Noe 2023 |
| Purchase Methods | ETH, USDT, BNB, MATIC and Card |
| Chain | Ethereum |
| Min Investment | None |
| Max Investment | None |
2. Bitcoin Minetrix – A Crypto Token With a 4 Billion Supply Cap Redefining the Future of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin Minetrix is a hot new deflationary token in the Bitcoin mining space. Within 10 days of launch, the platform has secured nearly $500,000, showing its potential and the growing interest from investors. The $BTCMTX token is central to the Bitcoin Minetrix ecosystem and is designed as a deflationary token. The ongoing presale has priced the token at $0.011, with a planned surge to $0.0119 by the final stage. With a total circulation of 4 billion tokens, 42.5% are allocated for mining, and 7.5% are set aside for staking. At the heart of Bitcoin Minetrix is its pioneering Stake-to-Mine model, a stark contrast to conventional Bitcoin mining.
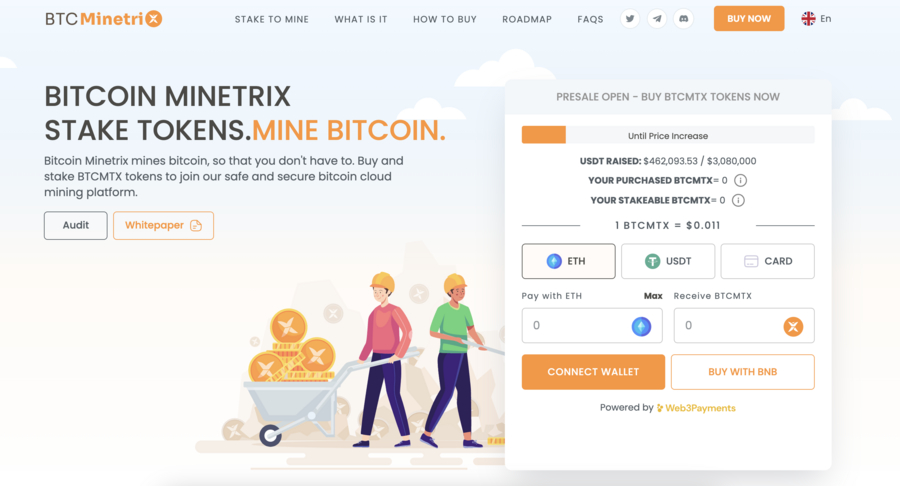
Traditional mining techniques involve energy-consuming hardware setups, which are financially and environmentally taxing. This has been a barrier for many users, but Bitcoin Minetrix offers a way out. Instead of heavy investments in machinery, users simply stake the platform’s native ERC-20 token, $BTCMTX, and receive non-tradeable mining credits. As these credits are burned, BTC rewards are accrued. Navigating the intricacies of Bitcoin mining can be daunting for many. Bitcoin Minetrix addresses this by integrating a user-friendly dashboard. This dashboard provides users with a comprehensive overview – from the BTC expected daily, weekly, or monthly to intricate details like hashing power and mining credits. Users can easily manage and monitor their mining operations on a desktop or mobile.

One of Bitcoin Minetrix’s standout features is its commitment to sustainability. The platform employs cloud mining, making it a green alternative in a sector known for its carbon footprint. Recognizing the importance of security, Bitcoin Minetrix has undergone third-party smart contract audits from Coinsult. A notable advantage of Bitcoin Minetrix is its emphasis on flexibility. Unlike traditional platforms where funds often get locked, users can unstake their $BTCMTX tokens anytime and sell them at prevailing market rates. Users interested in the project can stay updated by following Bitcoin Minetrix on X or entering its Telegram channel.
| Presale Started | 26 Sept 2023 |
| Purchase Methods | ETH, USDT, BNB |
| Chain | Ethereum |
| Min Investment | $10 |
| Max Investment | None |
5. Pikamoon – P2E Metaverse Crypto Burns 5% of the Tokens Spent on the NFT Marketplace
The next deflationary cryptocurrency on our list is $PIKA – the native token of Pikamoon. This is a play-to-earn metaverse environment, where players can purchase NFT, enter in battles, and earn rewards.  $PIKA is used to mint your own Pikamoon NFT companions – which is your entry point within the Pikaverse. In the virtual world, known as Dreva, players can access exploration and battle modes. Through exploration, players can capture new Pikamoon avatars to expand their empire. They can also explore 4 different regions of the world, and interact with NPCs. On the battle mode, you can leverage your NFT avatars in fights and earn rewards. To boost your winning chances, Pikamoon offers exclusive items from an NFT marketplace. Notably, 5% of all the tokens spent on the marketplace are burned. This helps reduce the supply, and makes the remaining tokens more valuable in the long run. Pikamoon also charges a 2.5% tax on all sell orders and transfers. Thus, this can help limit the token’s volatility. 0.5% of the tax collected is burned from the Pikamoon ecosystem. In total, Pikamoon has a total supply of 50 billion. 15 billion tokens have been allocated across three presale rounds. At the time of writing, $PIKA is priced at $0.0006 during the final stage of the presale. Once the presale ends, the token will be listed at a price of $0.0007.
$PIKA is used to mint your own Pikamoon NFT companions – which is your entry point within the Pikaverse. In the virtual world, known as Dreva, players can access exploration and battle modes. Through exploration, players can capture new Pikamoon avatars to expand their empire. They can also explore 4 different regions of the world, and interact with NPCs. On the battle mode, you can leverage your NFT avatars in fights and earn rewards. To boost your winning chances, Pikamoon offers exclusive items from an NFT marketplace. Notably, 5% of all the tokens spent on the marketplace are burned. This helps reduce the supply, and makes the remaining tokens more valuable in the long run. Pikamoon also charges a 2.5% tax on all sell orders and transfers. Thus, this can help limit the token’s volatility. 0.5% of the tax collected is burned from the Pikamoon ecosystem. In total, Pikamoon has a total supply of 50 billion. 15 billion tokens have been allocated across three presale rounds. At the time of writing, $PIKA is priced at $0.0006 during the final stage of the presale. Once the presale ends, the token will be listed at a price of $0.0007.  Pikamoon has raised over $4.2 million since the presale launched. Read the Pikamoon whitepaper and join the Telegram channel to learn more about this deflationary crypto.
Pikamoon has raised over $4.2 million since the presale launched. Read the Pikamoon whitepaper and join the Telegram channel to learn more about this deflationary crypto.
| Presale Started | May 2023 |
| Purchase Methods | ETH, USDT, BNB |
| Chain | Ethereum |
| Min Investment | N/A |
| Max Investment | None |
4. Bitcoin – Deflationary Cryptocurrency With a Cap of Just 21 Million BTC Tokens
Ever wondered what the best recession-proof crypto is? The de-facto digital asset of choice and global store of value – Bitcoin, is perhaps the best deflationary cryptocurrency to buy today. Founded in 2008 and launched in 2009, Bitcoin’s pseudonymous developer – Satoshi Nakamoto, wanted to create a decentralized payment network that could compete and overtake traditional fiat money. Today, Bitcoin is a multi-billion dollar asset class with more than 46 million holders in the US alone. One of the most attractive aspects of Bitcoin is that it is a deflationary asset with a limited supply of just 21 million tokens. This figure is expected to be reached in approximately 118 years. In the meantime, new Bitcoin tokens enter circulation on a 10-minute cycle. Initially, 50 BTC tokens were added to the circulating supply every 10 minutes, but this has since been reduced to 25 BTC, 12.5 BTC, and as of writing, 6.25 BTC. The reason for this is that periodically, the Bitcoin mining reward is halved. As such, the next Bitcoin halving – which is expected to happen in 2024, will reduce the 10-minute mining reward to 3.125 BTC.  Crucially, Bitcoin is viewed as a store of value rather than a medium of exchange and it carries even greater hallmarks than gold. For instance, Bitcoin can easily be transferred and stored, in addition to being split into small units. Perhaps the greatest challenge for Bitcoin at this moment in time is its proof-of-work crypto mechanism, which is detrimental to the environment. Nonetheless, considering that Bitcoin is still trading at an average of just $20,000, this is possible the best long-term cryptocurrency to buy. This represents a price discount of 70% from its previous high of over $68,000. As such, strong proponents of Bitcoin continue to buy into the project while prices remain low.
Crucially, Bitcoin is viewed as a store of value rather than a medium of exchange and it carries even greater hallmarks than gold. For instance, Bitcoin can easily be transferred and stored, in addition to being split into small units. Perhaps the greatest challenge for Bitcoin at this moment in time is its proof-of-work crypto mechanism, which is detrimental to the environment. Nonetheless, considering that Bitcoin is still trading at an average of just $20,000, this is possible the best long-term cryptocurrency to buy. This represents a price discount of 70% from its previous high of over $68,000. As such, strong proponents of Bitcoin continue to buy into the project while prices remain low.
5. BNB – Large-Cap Cryptocurrency With Frequent Token Burns
BNB – formally branded as Binance Coin, is the native cryptocurrency of the world’s large exchange. Launched in late 2017 at just over $0.10 per token, BNB is one of the best-performing cryptocurrencies of all time. Based on the all-time high it achieved in 2021, BNB has since increased in value by more than 6,000x. Not only is BNB used by traders on the Binance exchange to reduce commissions by 25%, but it offers a wide range of other use cases. This includes the ability to earn interest via staking. Moreover, BNB serves as the native currency of the Binance Smart Chain. As such, any transactions taking place on the network are settled in BNB.  The total supply of BNB is 200 million tokens. However, this is a deflationary cryptocurrency in nature, not least because Binance regularly burns tokens that are in circulation. Just a few days prior to writing, for example, Binance executed its 21st token burn. To date, nearly 40 million BNB tokens have been burned – which amounts to almost 20% of the total supply. Furthermore, and perhaps most importantly, the BNB token-burning program is self-sufficient. The reason for this is that Binance buys the respective tokens from the open marketplace using funds that have been raised from trading commissions. And, considering that Binance regularly attracts over $10 billion in daily trading volume, there is no reason to believe that its burning program will stop any time soon.
The total supply of BNB is 200 million tokens. However, this is a deflationary cryptocurrency in nature, not least because Binance regularly burns tokens that are in circulation. Just a few days prior to writing, for example, Binance executed its 21st token burn. To date, nearly 40 million BNB tokens have been burned – which amounts to almost 20% of the total supply. Furthermore, and perhaps most importantly, the BNB token-burning program is self-sufficient. The reason for this is that Binance buys the respective tokens from the open marketplace using funds that have been raised from trading commissions. And, considering that Binance regularly attracts over $10 billion in daily trading volume, there is no reason to believe that its burning program will stop any time soon.
6. XRP – Interbank Payment Network That Automatically Burns Transaction Fees
XRP could also be considered the best deflationary cryptocurrency to invest in right now. This project has been operational since 2012, which makes it one of the most established cryptocurrencies in the space. XRP primarily serves banks and financial institutions through its innovative payment network technology. The long-term objective of XRP is to replace the SWIFT network. XRP appeals to institutions that have a need to perform cross-border payments, not least because transactions take a matter of seconds to complete. Moreover, XRP can currently handle up to 1,500 transactions per second, irrespective of which currencies are being utilized in the transfer.
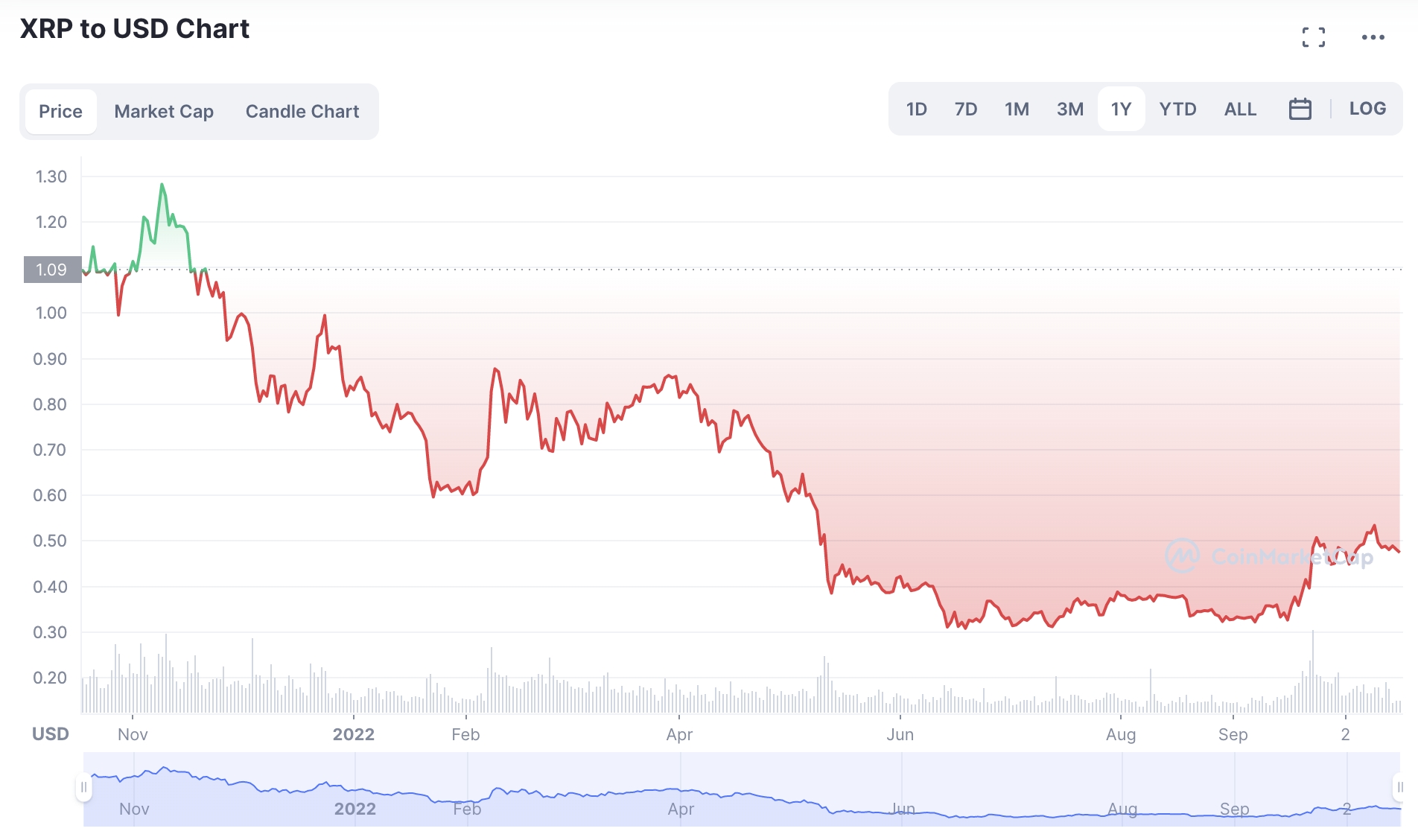
In terms of why this is a deflationary cryptocurrency, the XRP network automatically burns tokens associated with transaction fees. The standard transaction fee amounts to 0.00001 XRP which, although minute, could eventually translate into a sizable number of burned tokens – should its network be utilized by the global banking network. Those considering an investment in XRP will be pleased to know that the digital currency is trading at a huge discount when compared to previous highs making it one of the most undervalued cryptos on the market right now. Compared to its all-time high of $3.84 – which is achieved in 2018, XRP is trading at an 87% discount. As of writing, XRP is trading 65% below its 52-week high of $1.35.
7. Cronos – Proof of Authority Blockchain That Backs the Crypto.com Ecosystem
Cronos is the digital currency that backs the Crypto.com ecosystem. It operates on a proof of authority consensus mechanism, which ensures that transactions are fast, scalable, and cost-effective. In a similar nature to Binance’s BNB token, Cronos serves plenty of use cases. This includes offering traders of the Crypto.com exchange discounted trading fees. Cronos holders can also take advantage of higher APYs when utilizing Crypto.com crypto interest accounts or lower APYs when borrowing funds. Cronos can also be used to fund the Crypto.com debit card, which enables users to spend their digital assets in the real world. The overarching reason why Cronos is deflationary is that Crypto.com regularly engages in token burning.
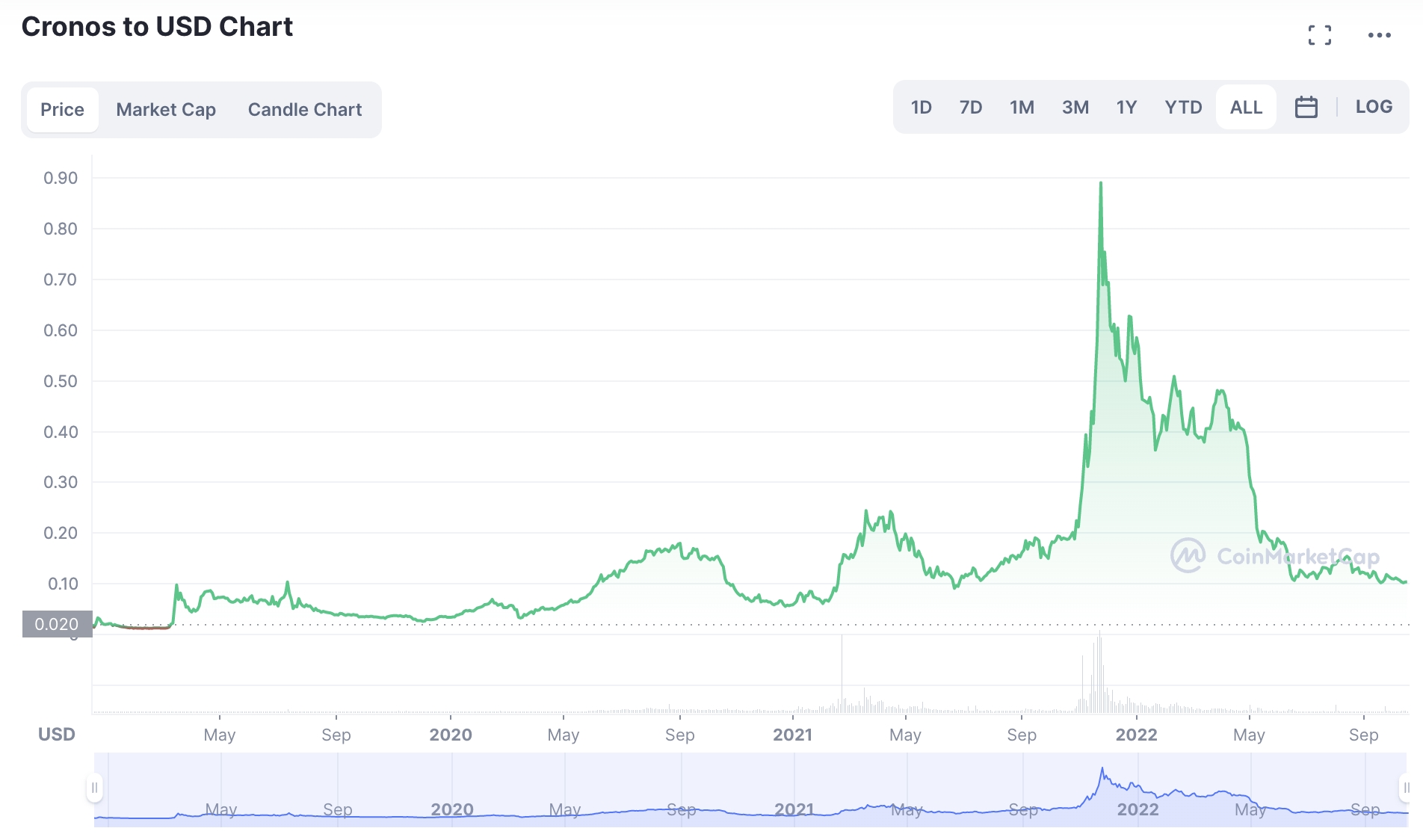
Many billions of Cronos tokens have been burned to date which many argue is reflected in the value of the cryptocurrency. For instance, CoinMarketCap notes that Cronos was originally trading at $0.02 when it hit public exchanges in 2018. The token hit an all-time high of just under $0.97 in 2021, representing growth of over 47x.
8. Shiba Inu – Meme Coin and Metaverse Project With a Deflationary Supply
Shiba Inu was created in 2020 as a meme coin alternative to Dogecoin. The project – which was created by an anonymous developer, very quickly amassed a huge online following via its social channels. This resulted in Shiba Inu becoming the fastest-growing cryptocurrency of all time. Although initial pricing data remain sketchy, Shiba Inu has since grown by several million percentage points. In fact, Shiba Inu is now a multi-billion dollar cryptocurrency and a top-15 project by market capitalization. Although the rise of Shiba Inu was largely built on speculation and FOMO, the project is looking to move away from its meme coin status. At the forefront of this is the project’s development of its very own metaverse world.
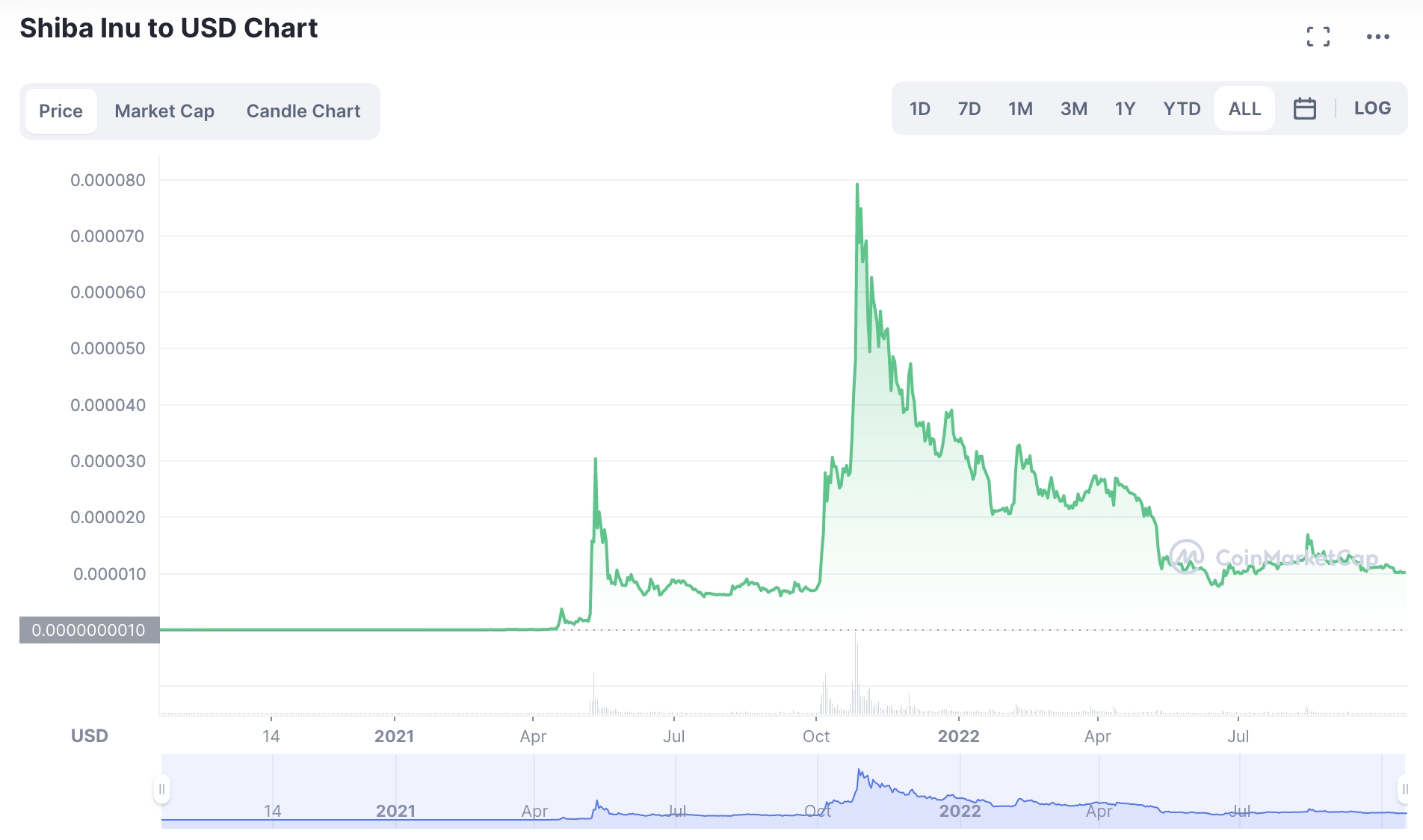
The Shibaverse will be home to many thousands of virtual plots that can be purchased by SHIB token holders. Each plot will be backed by NFT that operates on the blockchain. It remains to be seen if Shiba Inu will become the best metaverse coin, or if the likes of Decentraland and the Sandbox will continue to lead the way in this space. Nonetheless, when it comes to its deflationary crypto coins policies, Shiba Inu regularly burns tokens from its circulating supply. One such angle that the project is taking to fund its burning program is by utilizing 5% of any NFT sales to buy back tokens from the open marketplace.
9. PancakeSwap – Ongoing Burning Mechanism Reduces the Long-Term Supply of CAKE
PancakeSwap is the most popular decentralized exchange for the purpose of trading tokens that operate on the Binance Smart Chain. In the prior 30 days alone, PancakeSwap has been used by over 1.7 million. traders and more than $3.9 billion worth of crypto assets are locked in staking pools. Like most exchanges in this space, PancakeSwap has its own native token – CAKE. There are several use cases that CAKE token holders have access to. This includes the ability to provide liquidity to PancakeSwap pools, which enables investors to earn a share of any trading commissions collected by the exchange. CAKE holders also have access to higher-yield farming APYs.
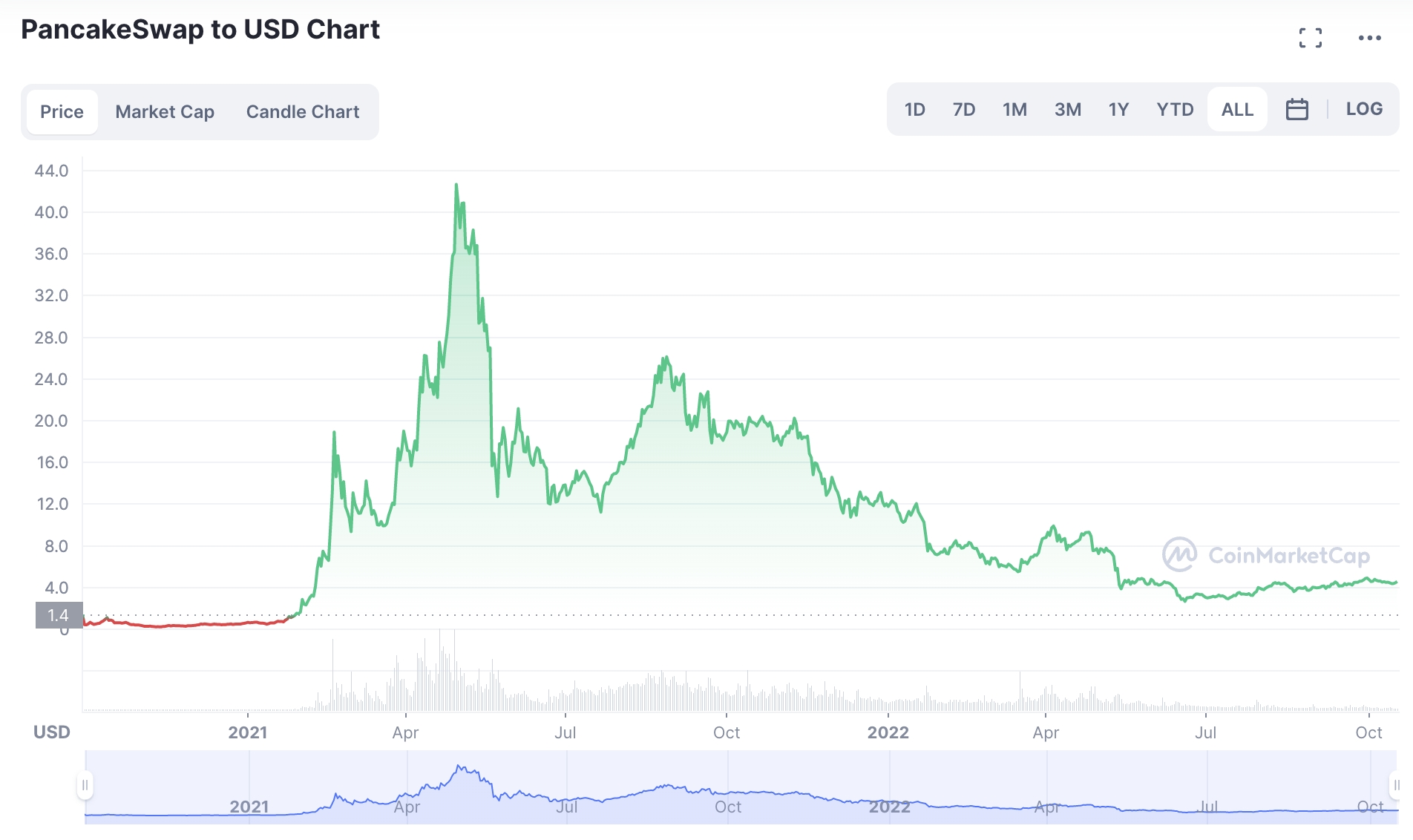
CAKE could also be viewed as an attractive addition to an investment portfolio considering how quickly the exchange has grown since launched in 2020. As of writing, CAKE carries a market capitalization of just over $650 million, so there is plenty of upside to target. Furthermore, investors might be attracted by the project’s regular token-burning mechanism. The objective outlined by PancakeSwap is to ensure that more tokens are being burned when compared to those entering circulation. This is an automated process based on many smart contract agreements. For instance, 10% of CAKE tokens utilized to buy lottery tickets on PancakSwap are subsequently burned.
10. Polygon – EIP-1559 Deployment Means That MATIC Fees are Burned
Polygon is a layer-2 scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain. This means that developers can build decentralized applications via the Ethereum framework in a cost-effective and scalable way. Polygon has its own native cryptocurrency – MATIC, which now carries a multi-billion dollar market capitalization.
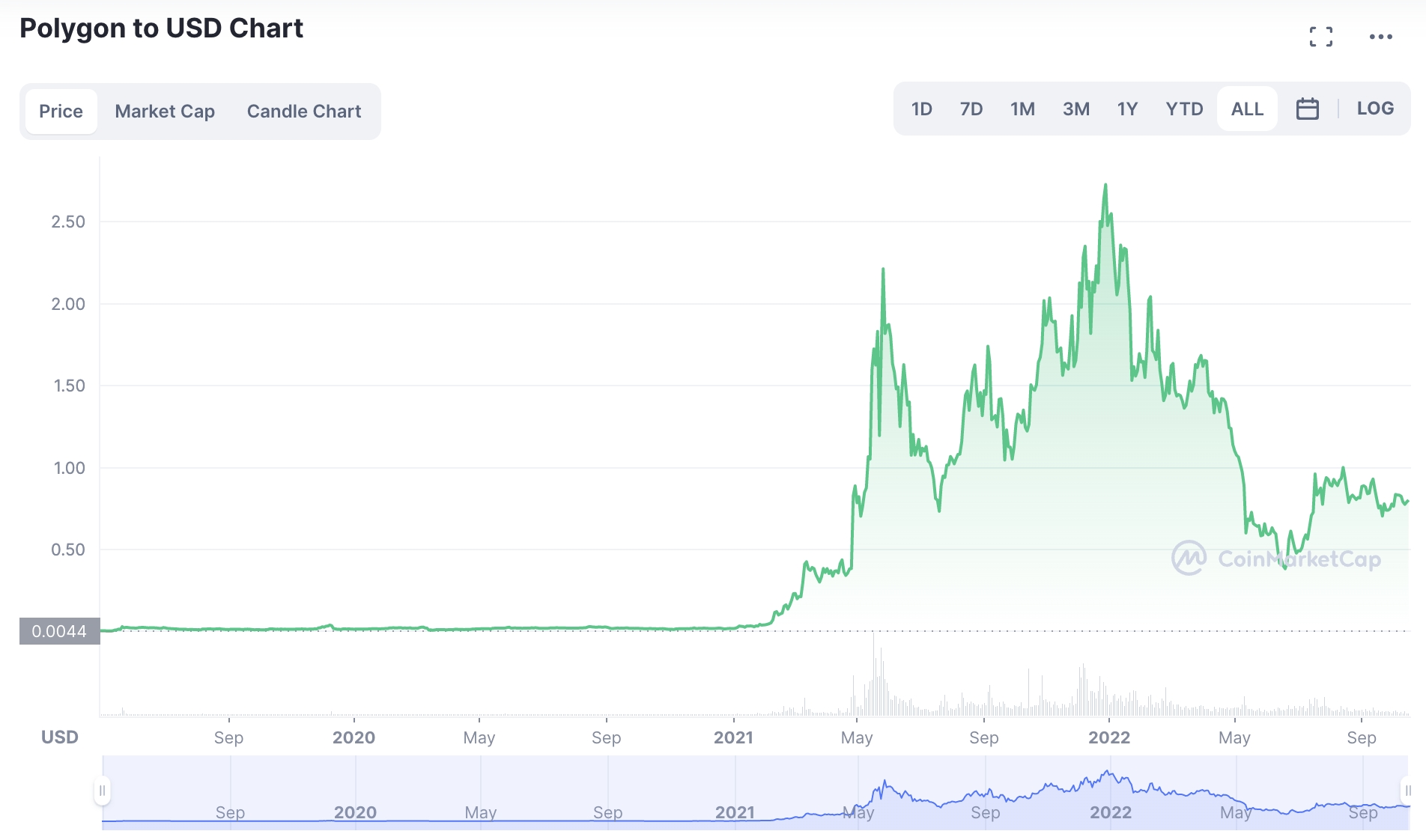
Since migrating to the EIP-1559 standard, Polygon is a deflationary digital asset. The reason for this is that when transaction fees are paid in MATIC, the tokens are subsequently burned from the circulating supply. Polygon has a total supply of 10 billion tokens and as of writing, MATIC is trading at a 72% discount from its 52-week high.
What is Deflationary Crypto?
In a nutshell, deflationary cryptos are digital assets that have a decreasing supply. This means that over the course of time, fewer tokens will remain in circulation. This is in stark contrast to traditional fiat currencies like the US dollar and euro, which are inflationary. The reason for this is that the Federal Reserve and European Central Bank regularly print new money, which subsequently enters the supply. As a result, fiat currencies consistently lose value as per the impact of inflation. Deflationary cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, do the complete opposite. In theory – and assuming that the respective token retains its demand, the value of a deflationary cryptocurrency will rise over time. This is because the cryptocurrency becomes scarcer, which can have the potential to increase its value as the supply is reduced. Some of the best deflationary cryptocurrency projects that we discussed on this page include Bitcoin ETF Token and Bitcoin. These also happen to be some of the best cryptos to buy during the crash.
Why Invest in Deflationary Tokens?
Deflationary cryptocurrencies may appeal to long-term investors for a wide range of reasons – which we discuss in more detail in the sections below.
Inflationary Cryptocurrencies Diminish in Value
The easiest way to assess the benefits of investing in deflationary cryptocurrencies is to first understand the drawbacks of their inflationary counterparts.
- As a prime example, Dogecoin is an inflationary cryptocurrency.
- The reason for this is that Dogecoin increases the supply of its token by 10,000 DOGE for each block that is minted.
- This translates into 5 million new Dogecoin tokens each and every year.
- As a result, the true value of Dogecoin continues to decline as every year passes.
This is much the same as holding US dollars in a bank account. Considering the unprecedented inflation crisis currently facing global economies, cash continues to lose its value.
Supply Decreases Over Time
In contrast, the best deflationary tokens offer an attractive long-term outlook. Crucially, this is because the overall supply of the token will continue to decline. As noted earlier, the likes of Bitcoin ETF Token operate deflationary policies, which means that tokens regularly leave the circulating supply. Bitcoin ETF Token, for example, burns 5% of every transaction plus 5% of the total supply with one of the five milestones. The theory is that if the supply of the token continues to decline and demand remains consistent, then the value of the cryptocurrency will increase.
- This is much the same as a share buyback program initiated by publicly traded stocks.
- When the company in question utilized free cash flow to buy back its own shares, this typically has the desired impact of artificially increasing the value of the stock.
Many Mechanisms to Reduce the Supply
The best deflationary cryptocurrency projects have many options when it comes to reducing the overall supply of their token. This includes:
Burning
One of the main ways that projects reduce their token supply is through regular token burns. The tokens are sent to a ‘burn wallet’ that cannot be accessed under any circumstances, which essentially removes them from the supply.
Buy Back
Some cryptocurrency projects will utilize funds raised from their respective products and services to buy back the token from the open marketplace. As noted above, this is much the same as a traditional stock buyback program. This system is utilized by Binance, which buys BNB back from the market with the fees it collects from trading commissions.
Transaction Fees
Another method that the best deflationary cryptocurrency projects utilize to reduce the supply of their token is to burn transaction fees. This means that when the sender pays for a transaction in the native cryptocurrency, the tokens leave the circulating supply. This method is utilized by the likes of Polygon and XRP.
Conclusion
In summary, deflationary cryptocurrencies appeal to investors largely because the overall supply of tokens will reduce over time. Assuming that demand for the token remains intact, the theory is that deflationary cryptocurrencies will continue to increase in value as the supply declines. With up to 25% of the total supply set for burning, we recommend Bitcoin ETF Token as one of the top investments right now. At press time, $BTCETF is priced at $0.0050 on presale.
FAQs
What is deflationary cryptocurrency?
Deflationary cryptocurrencies are those that over the course of time, will see their circulating supply decrease. In turn, if demand for the token increases, this can have the desired impact of increasing the cryptocurrency’s value. After all, if there are fewer tokens available in the market and demand is on the up, naturally, its value will rise.
What cryptocurrencies are deflationary?
Examples of deflationary cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, BNB, XRP, Shiba Inu, and Polygon. Newer deflationary projects worth a look at include $BTCETF, and $BTCMTX.
Is a deflationary crypto good?
On the one hand, buying a cryptocurrency that is deflationary will not necessarily result in greater gains when compared to inflationary alternatives. For instance, although Ethereum was inflationary for seven years before its recent PoS merge, it still remained the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. However, holding deflationary cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Bitcoin ETF Token is likely a better strategy in the long run. After all, investors do not need to worry about the risk of inflation.
What is the best deflationary cryptocurrency?
Overall, we found that Bitcoin ETF Token ($BTCETF) could be one of the top cryptocurrency tokens to consider buying. It has a supply cap of 4 billion with an affordable token price during the presale.
Is Ethereum deflationary?
Prior to its recent transition to proof-of-stake, Ethereum was an inflationary cryptocurrency. This is because each year, new tokens entered circulation. However, since the merge, Ethereum is now a deflationary cryptocurrency. In addition to its solid smart contract ecosystem, this makes Ethereum even more attractive.
Is Bitcoin deflationary?
Put simply, yes – Bitcoin is deflationary. The world’s largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization releases new BTC tokens into circulation every 10 minutes. This will continue to be the case until Bitcoin reaches a total supply of 21 million. At this point, no additional BTC tokens will ever enter circulation.
About Cryptonews
At Cryptonews, we aim to provide a comprehensive and objective perspective on the cryptocurrency market, empowering our readers to make informed decisions in this ever-evolving landscape.
Our editorial team, comprised of more than 20 professionals in the crypto space, works diligently to uphold the highest standards of journalism and ethics. We follow strict editorial guidelines to ensure the integrity and credibility of our content.
Whether you’re seeking breaking news, expert opinions, educational resources, or market insights, Cryptonews.com is your go-to destination for all things crypto since 2017.







 Sergio Zammit
Sergio Zammit 

 Eric Huffman
Eric Huffman