Loom Network and LOOM token form the backbone of this dApp scaling platform for Ethereum. The Loom focuses on games and social media apps which are provided with sidechains to improve their scalability and throughput.

What Is Loom Network?
Self-described as the “next-gen blockchain application platform for Ethereum”, the Bangkok-based Loom Network was launched in 2017 with the mission to become an equivalent of EOS which would be compatible with Ethereum and secured by its native features. It basically functions as the network of sidechains running on the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus algorithm. Based on this architecture, the network promotes itself as a Layer 2 scaling solution which allows for the development of scalable decentralized apps (dApps) and blockchain-based games, with an added bonus of security provided by the Ethereum mainnet.
What Is Loom Trying to Achieve?
The Loom network is built around several key features which should allow its developers to present them as solutions to the issues facing the blockchain technology of today:
- Loom wants to allow for the creation of decentralized applications which would scale much easier than it is possible today. DApps sometimes have a hard time scaling successfully, primarily due to their competition for available resources with other DApps and financial transactions. At the same time, all the apps need to be provided with an identical level of security. In response to this, the Loom network provides the developers with an opportunity to use DAppChain technology which, in essence, functions as a DApp which is being run as a sidechain. Based on this, transactions on the DAppChain become relevant only to an individual DApp, allowing it to handle a higher number of them in the long run. In addition to this, the developers are expected to be drawn to the Loom based on its lower costs of development and more computing power at their disposal.
- Loom wants to make DApps more shareable and transparent. Based on its implementation of the DAppChain technology, the nodes in the Loom network can be run in order to provide the users with a copy of the stored user data which is kept on the blockchain. This approach should allow the Loom developers to have an easier time when, for example, they want to create a game sequel. In this case, they would just need to source data from the earlier iterations of the game in form of information on digital assets, characters etc.
- The DApps built on the Loom should also offer better security and become manageable in a more democratic manner. As the Loom network consists of a decentralized chain of communities, there is no opportunity for the central authority to attempt to shut these down or try to censor the games and other types of content without the general consensus. The communities can use their voting rights to decide if the DApps running on the chain are acceptable for them or not. Finally, they are also free to opt for forking in case of an unpreventable attack.
How Does Loom Work?
In order to be able to deliver on these promises, the Loom platform features several main components which make up its ecosystem:
- The Loom software development kit (SDK)
- DAppChains
- DPoS mechanism
- Plasma technology
- Loom token
The Loom software development kit is designed to function as both the foundation block of the network and a DIY tool for the creation of its building elements. The SDK makes it possible for the developers to code and deploy DApps and games based on the Ethereum blockchain, without requiring them to possess advanced knowledge of the blockchain infrastructure itself. In the long run, even the individuals without the professional background as developers should be able to get the job done with the help of the Loom.
How Do DAppChains Work?
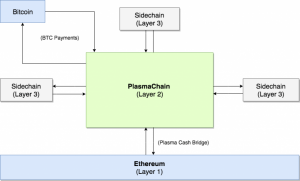
The SDK on the Loom is only a piece of the puzzle. Whatever the developers (or the non-developers) create with its help, it needs to be deployed on the DAppChains. These function as sidechains for Ethereum with an application-specific mode of operation. In essence, a DApp which gets created on the Loom will have its dedicated DAppChain, while the chains as a group will make up the bulk of the Loom Network. Access to it will be provided with the use of the LOOM tokens (see below). At the same time, the DAppchains will be connected with the Ethereum mainnet smart contract system which regularly records the state of DAppchains.
Having a dedicated sidechain to Ethereum for an individual DApp allows developers to establish their own datasets and consensus rulesets autonomously, while bypassing the performance bottlenecks which plague the Ethereum’s main chain. Since the DAppChain operates as a Layer 2 chain on the base layer provided by the Ethereum, the security benefits of the main platform can still be reaped. This encompasses the assets on the DAppChain, such as ERC20 tokens.
With this approach, Loom aims to benefit the Ethereum platform as well. As the majority of the computation load is done on the side chains, scaling should be easier in parallel with placing less burden on the main blockchain. This should prevent the bloating of the Ethereum chain and help it scale better while keeping its base layer decentralized.

How Can DPoS Help Loom?
The Loom platform wants to go beyond the Proof of Stake implementation which is said to be planned for Ethereum. While Ethereum aims to introduce this to eliminate the need for each node to process and store every transaction, the Loom team decided that while this option would still hamper decentralization efforts by allowing the stake owners to stake more and more frequently based on what they already have.
Instead of this, the Loom SDK will offer out-of-the-box support for the Delegated Proof of Stake which should allow the DApps to implement transactions without “gas” and offer faster transaction times. Based on this system, the users will be able to vote to protect the platform’s impartiality and enjoy faster performance compared to the Proof of Work, for example. At the same time, the developers are still allowed to choose whichever consensus mechanism they deem suitable for their project.
One of the first massively scalable implementations of the Loom technology is the Zombie Battleground which is touted as the world’s first fully blockchain-based game. The Loom team compares its case to the one involving CryptoKitties, a game which, according to them, demonstrated the weakness of the Ethereum platform to handle even a simple game.
In addition to games, another well-known implementation of the DAppChains is DelegateCall, a Q&A platform in which the users can earn tokens by asking and answering questions. It was the first DAppChain which went live on the Loom.
How Can Plasma Help the Loom Deliver Better Security?
Having the DPoS as the main consensus mechanism on the Loom platform did not satisfy its developers in terms of having a complete solution for the protection of digital assets and offering full-blown scalability and decentralization. The solution was found in integrating the DPoS sidechains with the Plasma i.e. Plasma Cash technology:
- Plasma emerged as the technology focused on enabling secure deposits and withdrawals between multiple blockchains.
- In order for the DAppChains to fully deliver on their promise of scalability, this required making trust assumptions. While the DPoS and its witness system protected their decentralization aspect, the Loom team decided to go for Plasma as the guarantee of automated security for both public and private chains.
- In case of Loom, Plasma makes it possible for the users to transfer their digital assets from the Ethereum mainnet to sidechains in an arguably secure manner. This can be done without the obligation to trust the consensus mechanism found on a particular sidechain. The asset owners would be provided with a more secure system capable of supporting multiple critical operations taking place on the blockchain.
- The first implementation of Plasma on the Loom involved the support for the transfer of the Ethereum-based tokens onto the Loom sidechains without compromising the security offered by the main platform. Each token deposited onto the sidechain was given a unique serial number, with the token itself being non-fungible and having its own transaction history.
- The system is described as being particularly beneficial for games which can safely run on a sidechain while their Plasma exits provide access to the funds and game-based assets on the Ethereum blockchain. In case of a hacking attack, for example, these can be securely recovered and made ready for future use. The Loom team plans to implement the same approach to the mobile games which would be run on sidechains while their items and other collectibles would be kept on the Ethereum mainchain.
Loom Token Economics
Loom token is an ERC20 token used to pay for the membership in the Loom network. This entails the use of both the platform and any app featured on it, as well as the transfer of assets from the network onto the Ethereum mainnet. Before initiating a transfer, the DApp on the Loom will check if the users have enough LOOM in their wallets. Loom can be also used as in-game currency for any such product launched on the Loom.
As of April 2019, the currency’s market cap stood at just above USD 61 million, down from its historic high of USD 376 million in May 2018. At the same time, more than 778 million tokens were in circulation, out of the planned total supply of one billion tokens. LOOM is readily available for trading on the cryptocurrency exchanges such as Binance and Bittrex. Acquired tokens can be stored in any wallet which supports ERC-20.
The Loom Network is based in Bangkok, with the project team having more than 50 core members. The project’s CEO is a software development and programming veteran Matthew Campbell, who founded the project together with James Martin Duffy and Luke Zhang.