What is the Metaverse?
Since the creation of the internet, multiple novels, movies and video games have been released detailing living alternate realities in interconnected networks. After initially being popularized in the early ’90s, it has now regained traction in the current technological discourse under the term “metaverse”. In a nutshell, the metaverse represents a virtual realm where users can interact, create, and engage in immersive experiences.
So what would the Metaverse mean for the world, and what are its effects on cryptocurrency and NFTs? Throughout this guide, we explore key concepts surrounding the Metaverse, taking stock of its origins, defining features, and implications for society. From decentralized networks to virtual economies, we’ll cover essential aspects of this evolving digital landscape so that we can give as comprehensive an answer as we can to the question “What is the Metaverse?”
What Does ‘Metaverse’ Mean?
In recent years, the term “Metaverse” has experienced a surge in mainstream adoption, capturing the imagination of both tech enthusiasts and the general public alike. Coined by science fiction author Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel, “Snow Crash,” the concept of the Metaverse has evolved from a fictional virtual world into a tangible vision of the future.
Today, the Metaverse refers to a collective virtual space that encompasses all virtual environments, augmented reality, and the internet as a whole. It represents a convergence of digital and physical realities, where users can interact with each other and digital objects in real time.

This concept has gained significant attention from major tech companies, including Facebook (now Meta), which announced its rebranding in October 2021 to emphasize its commitment to building the Metaverse. Other industry giants like Microsoft, Google, and Epic Games have also expressed interest in developing Metaverse-related technologies and platforms.
The growing interest in the Metaverse is not limited to the tech industry. Financial institutions, entertainment companies, and even governments are exploring the potential applications and implications of this virtual realm. As a result, discussions about the Metaverse have become increasingly prevalent in mainstream media, shaping public perceptions and fueling curiosity about its possibilities.
How Does the Metaverse Work?
Now that we’ve explained the basics and current landscape of the Metaverse let’s build our understanding of how it works. The Metaverse operates through a combination of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, along with blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and other emerging technologies. Users access the Metaverse through specialized hardware like VR headsets or traditional computing devices.
In the Metaverse, users can interact with each other and the environment, create content, buy and sell virtual assets, attend events, and much more. The underlying infrastructure relies on decentralized networks to ensure the security, integrity, and persistence of the virtual world.

The process of how the Metaverse works begins with the creation of these immersive virtual environments where users can interact with each other and digital assets in real-time. These environments are built on virtual platforms that leverage advanced graphics and rendering technologies to create realistic and fantastical worlds. Users navigate these virtual spaces using customizable digital avatars, which serve as their digital representations within the Metaverse.
One of the defining features of the Metaverse is its decentralized nature, which is facilitated by blockchain technology. Blockchain enables the secure and transparent exchange of digital assets, ownership records, and transactions within the Metaverse. This decentralization ensures greater autonomy, security, and control over digital assets for users.
Furthermore, the Metaverse fosters social interaction and collaboration through various virtual communities, events, and activities. Users can engage in real-time communication, participate in virtual events, and collaborate on projects within the Metaverse. Additionally, the Metaverse offers economic opportunities through virtual commerce, digital asset trading, and the creation of virtual goods and services.
Defining Features of the Metaverse
The Metaverse is made unique by its collection of features and functionalities, includingits use of decentralization, artificial intelligence (AI), avatars, and immersive environments. To better understand what makes the Metaverse what it is, let’s explore its main defining features.
Decentralization
Decentralization is a core feature of the Metaverse, ensuring that no single entity has control over the entire virtual environment. Blockchain technology plays a significant role in achieving decentralization by enabling peer-to-peer transactions, ownership verification, and governance mechanisms without the need for intermediaries.
For instance, Decentraland, a prominent virtual world platform, utilizes blockchain to empower users with land ownership, voting rights, and control over in-world assets, fostering a truly decentralized ecosystem.

Avatars
Avatars are digital representations of users within the Metaverse. Users can customize their avatars to reflect their identities, preferences, and personalities. Avatars enable social interactions and immersion within the virtual environment, allowing users to express themselves and engage with others.
Take, for example, VRChat, a popular virtual reality platform where users create and customize avatars to navigate virtual spaces, attend events, and engage in conversations with fellow participants. Avatars not only enhance user engagement but also foster a sense of presence and belonging within virtual communities.
Immersive Experiences
Immersive experiences are a hallmark of the Metaverse, providing users with rich, interactive environments that mimic the real world or transcend its limitations. From virtual concerts and art exhibitions to educational simulations and business meetings, the Metaverse offers a myriad of immersive experiences.
For instance, Fortnite’s in-game concerts, featuring renowned artists like Travis Scott and Marshmello, attract millions of players worldwide, blurring the boundaries between gaming and entertainment. These immersive events showcase the Metaverse’s potential to revolutionize entertainment, education, and social interaction on a global scale.
Use of AI
Artificial intelligence enhances the functionality and realism of the Metaverse by powering intelligent NPCs (non-player characters), personal assistants, automated content creation tools, and more. AI algorithms also contribute to dynamic world-building, adaptive gameplay, and personalized experiences.
For example, AI-driven chatbots in virtual environments like Second Life assist users with navigation, information retrieval, and social interactions, enriching the overall user experience. Additionally, AI-driven content generation tools enable creators to produce lifelike environments, characters, and narratives, further enhancing the Metaverse’s immersive appeal.

Creator Economy
The Metaverse fosters a vibrant creator economy where users can monetize their skills, creations, and experiences. Creators can sell virtual goods, offer services, host events, and engage with their audience, opening up new avenues for entrepreneurship and self-expression.
For example, gaming platforms like Minecraft enable users to design and sell virtual items, create custom game modes, and organize virtual events, fostering a vibrant ecosystem of creators and consumers. The creator economy within the Metaverse not only provides economic opportunities but also fosters creativity, collaboration, and innovation on a global scale.
Click here to find out more about the best Metaverse games in 2024.
Persistence
Persistence ensures that changes made within the Metaverse persist over time, allowing for continuity and long-term engagement. Blockchain technology facilitates asset ownership, digital scarcity, and verifiable transactions, ensuring that user contributions are preserved and recognized.
For instance, Cryptovoxels (Voxels), a virtual world platform built on Ethereum, leverages blockchain to ensure permanent land ownership and asset interoperability, allowing users to build, trade, and showcase digital creations seamlessly. The concept of persistence within the Metaverse reinforces the notion of digital ownership and fosters trust and reliability among users.
How Do You Access the Metaverse?
Accessing the Metaverse involves both hardware and software components. On the hardware side, users typically need a device capable of running virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) applications, such as VR headsets, AR glasses, or powerful computers with compatible peripherals.
Popular virtual reality technology includes headsets like the Oculus Rift, Meta Quest 3, and PlayStation VR offers immersive experiences, while AR glasses like Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap provide mixed-reality interactions. Additionally, smartphones and tablets equipped with AR capabilities can also serve as entry points to the Metaverse. Apple also launched its own VR headset, the “Vision Pro,” earlier this year and has already started exploring ways to bring crypto trading to the Metaverse.

Moving away from the hardware, software also plays a crucial role in accessing the Metaverse, with various virtual worlds, platforms, and applications offering immersive experiences. Platforms like Decentraland, Cryptovoxels, and Roblox provide virtual environments where users can interact with each other and create or purchase digital assets.
Social VR applications like VRChat and AltspaceVR enable users to socialize, attend events, and explore user-generated content. Furthermore, web-based platforms like Spatial and Mozilla Hubs offer browser-based access to virtual spaces, making the Metaverse more accessible to a broader audience.
Access to the Metaverse varies in terms of cost, depending on the hardware and software requirements. While some platforms and applications offer free access with basic features, others may require users to purchase premium subscriptions, digital assets, or virtual land for full access and enhanced experiences. You may also need to pay transaction fees depending on the network used, For instance, Decentraland provides free access to its virtual world, but users need to buy MANA tokens to obtain land, items, and other assets within the platform. In addition to this, you will need to factor in the costs of a VR headset, subscription fees, and in-app purchases that may apply to access certain experiences and applications. At present, Meta’s Quest 3 headset costs start at $500, the HTC Vive $450, and the Apple Vision Pro retailing for over $3,400. As the technology begins to improve with the cost of production lower, it is likely that the price of headsets will significantly fall. The current landscape of the Metaverse is characterized by a blend of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and various online platforms that offer immersive digital experiences. While the concept of the Metaverse is still evolving, several real-world examples showcase its potential across different industries. One notable example is Fortnite, which is a popular online multiplayer game developed by Epic Games. Fortnite’s virtual concerts, such as the one featuring artist Travis Scott in 2020, attracted millions of players who experienced a groundbreaking blend of music, gaming, and virtual reality. These events demonstrated how the Metaverse can be leveraged for large-scale entertainment and social gatherings. Read our guide to find some more of the top Web3 games similar to Fortnite. Another example comes from the world of education, where platforms like Minecraft have been used to recreate historical landmarks and facilitate immersive learning experiences. For instance, the Block by Block initiative, supported by the United Nations and Mojang Studios, aims to empower communities by enabling them to design and build public spaces within the game. By leveraging Minecraft’s creative tools, participants can collaborate on architectural projects and envision sustainable urban environments, showcasing the educational potential of the Metaverse. Overall, these examples offer a glimpse into the diverse applications of the Metaverse across entertainment, fashion, education, and business. As technology continues to advance and more companies embrace virtual experiences, the Metaverse is poised to become an integral part of our digital lives, offering endless possibilities for creativity, innovation, and connectivity. Cryptocurrency plays a pivotal role in the Metaverse, acting as the backbone of its economic infrastructure and facilitating seamless transactions within virtual environments. At the heart of this integration is blockchain technology, which provides the foundation for decentralized systems, secure transactions, and digital ownership. One of the key functions of cryptocurrency in the Metaverse is as a medium of exchange for digital assets, virtual goods, and services. In virtual worlds like Decentraland and Cryptovoxels, users can purchase land, avatars, virtual clothing, and other digital items using cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum (ETH) or specific in-game tokens like MANA. These transactions are executed on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency, immutability, and security. Moreover, cryptocurrencies enable the creation and trading of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which are unique digital assets representing ownership or proof of authenticity for items such as artwork, collectibles, and virtual real estate. NFT marketplaces like OpenSea and Rarible have flourished within the Metaverse, allowing creators to tokenize their creations and buyers to acquire rare and valuable digital assets. Furthermore, cryptocurrency fosters interoperability across different virtual platforms and ecosystems within the Metaverse. With blockchain-based standards like ERC-20, users can seamlessly transfer assets and data between various applications and games, regardless of their underlying protocols. This interoperability enhances user experiences and encourages innovation within the Metaverse by enabling cross-platform interactions and collaborations. In essence, the blockchain serves as the lifeblood of the Metaverse, powering its economy, enabling digital ownership, and fostering innovation in virtual environments. As the Metaverse continues to evolve and expand, cryptocurrency will remain an integral component, driving its growth and unlocking new opportunities for users and creators alike. Virtual reality (VR) is a key component of the Metaverse as it provides the immersive interface through which users experience its digital realms. VR technology, headsets, and motion controllers allow you to step into a digital al world that mimics or completely reimagines physical spaces. In the Metaverse, VR not only enhances visual and auditory sensations but also gives users a tangible sense of touch and enhances the realism of their interactions. As VR technology advances, it will continue to blur the lines between the digital and physical worlds, offering more seamless and intuitive experiences. Companies like Meta, Apple, and HTC are at the forefront, continually pushing the boundaries of what VR can achieve within the Metaverse, making it more accessible and engaging for a global audience. There are a vast number of future use cases for the Metaverse. These cover everything from shopping, healthcare, gaming, and even education. Let’s take a look at some of these in more depth. In the future, shopping in the Metaverse will transcend traditional online shopping carts and product images, offering interactive and social experiences. Brands like Nike and Gucci have already begun experimenting with virtual stores where users can try on digital clothing or shoes on their avatars before purchasing the physical item. As mentioned earlier in the guide, Gucci was selling sneakers for $17.99 on the Metaverse, with multiple brands likely to adopt similar services in the future. When it comes to gaming in the Metaverse, this will likely move beyond the current confines of the screen to become a fully immersive experience. Popular games like Fortnite are already pioneering this shift, creating expansive worlds where gaming is just one aspect of the user experience, and entertainment and shopping are also used as a way to engage gamers. Future Metaverse gaming could include full-body interaction, where every physical action is mirrored in the game, providing a level of immersion that traditional controller-centered gaming cannot match. The Metaverse promises to transform healthcare by offering remote consultations, virtual surgeries, and medical training programs that utilize VR to simulate real-life operations. This could democratize access to high-quality healthcare, particularly in underserved regions, and enhance the training of medical professionals, allowing them to practice techniques in a risk-free, controlled environment. Educational applications in the Metaverse are particularly promising. Virtual classrooms can replicate and enhance face-to-face learning, enabling students from around the world to interact as if they were in the same room. Historical recreations, scientific simulations, and virtual field trips can all be more engaging and informative, offering students immersive learning experiences that are not possible today. While often used interchangeably with mainstream media, Web3 and the Metaverse are not the same thing. Web3 refers to the third generation of internet services for websites and applications that incorporate concepts including decentralization, blockchain technologies, and token-based economics. It represents a move towards a more user-owned, privacy-focused internet. On the other hand, the Metaverse is a collective virtual shared space created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical and digital reality. It provides a sense of continuity and real-time existence regardless of user presence. Although the Metaverse utilizes many Web3 technologies, it is more focused on creating immersive, interactive worlds. Understanding the distinctions and connections between Web3 and the Metaverse is crucial as both will likely play significant roles in shaping the future of digital interaction. As these technologies develop, their paths will increasingly intertwine, leading to new possibilities and innovations that could fundamentally change how we interact with the digital world. The Metaverse is rapidly evolving, with numerous technology companies leading the charge in its development and growth. Let’s take a brief look at some of the key players in this space. With any groundbreaking technology, there are both positives and negatives associated with it, the Metaverse is no different. Let’s go over all the advantages and disadvantages of this revolutionary breakthrough. Starting with the advantages, the Metaverse offers several potential pros, including: Regarding its disadvantages, the Metaverse also poses certain challenges and drawbacks. The Metaverse presents a mixture of advantages and disadvantages that shape its impact on society and individuals. On the one hand, the Metaverse offers unparalleled immersive experiences, global connectivity, and creative expression. Users can enjoy immersive virtual environments, connect with people from around the world, and express themselves creatively through avatar customization and virtual art. Additionally, the Metaverse creates new economic opportunities for entrepreneurship, innovation, and education. However, the Metaverse also comes with its share of challenges. Privacy concerns, digital divide issues, and the risk of escapism and addiction pose significant drawbacks to widespread Metaverse adoption. Furthermore, regulatory uncertainties and technical limitations may hinder the Metaverse’s development and accessibility for all users. Should it become widely available to society, the Metaverse has the potential to profoundly impact various aspects of everyday life. These include: The Metaverse represents a shift in how we interact with digital environments, offering immersive, interconnected, and persistent virtual worlds. With its potential to revolutionize social interaction, entertainment, education, commerce, and more, the Metaverse is indeed here to stay. However, realizing its full potential will require addressing various challenges, including issues related to accessibility, privacy, security, and regulation. As technology continues to evolve and society adapts to new digital realities, the Metaverse will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of human experience. To learn more about the Metaverse, read our guide on the best Metaverse casinos in the market. The metaverse is a collective virtual space created by the convergence of digital technologies, where users can interact with each other and digital environments in real time. The purpose of the metaverse is to provide a shared virtual space where users can socialize, work, play, and engage in various activities similar to the physical world. While the metaverse is accessible to anyone with an internet connection and compatible devices, the extent of access and participation may vary depending on factors such as affordability, platform restrictions, and technological access. To get into the Metaverse, you typically need a smartphone, computer, or virtual reality headset. You can then connect to Metaverse platforms or applications where you can create avatars, explore virtual environments, and interact with other users. Access to the metaverse may be free on some platforms or applications, while others may require subscription fees, in-app purchases, or virtual currency for certain features, content, or experiences. No, Mark Zuckerberg is not the owner of the Metaverse. However, Facebook, now Meta Platforms is one of the companies heavily investing in Metaverse development. The Metaverse is a decentralized and interconnected digital space, meaning it doesn’t have a single owner. Instead, it’s shaped by the collective contributions of developers, users, and organizations across various industries. Yes, the Metaverse exists as a concept and is continually evolving with advancements in technology and the development of virtual environments, platforms, and applications. There isn’t a definitive number of Metaverses, as the concept covers a wide range of virtual spaces, platforms, and applications. Different companies and developers are building their own versions of the Metaverse, each with its unique features, communities, and experiences.Is it Free to Access the Metaverse?
What Does the Metaverse Look Like Right Now?

In the realm of fashion, luxury brand Gucci launched its own virtual sneakers costing $17.99 on the AR-based fashion technology platform called Wanna. Users can try on virtual sneakers using their smartphones, providing an interactive shopping experience that blurs the line between the physical and digital worlds. This initiative exemplifies how brands are exploring innovative ways to engage consumers and drive sales in the Metaverse.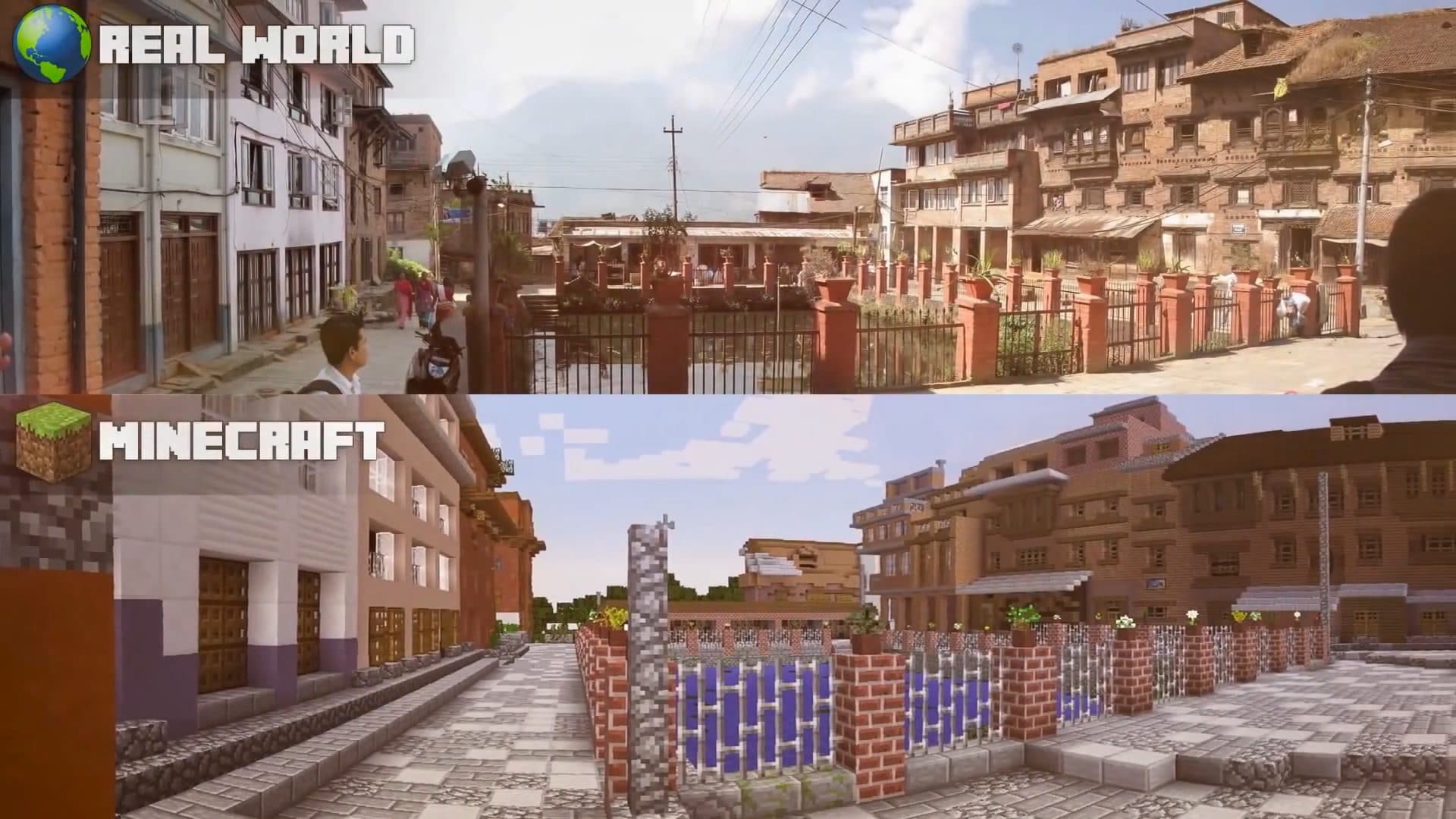
In the business sector, virtual reality platforms like Spatial have gained traction for remote collaboration and communication. Spatial allows users to meet in virtual spaces, share documents, and interact with 3D models in real time, fostering a more immersive and productive remote work environment. Companies like Pfizer and Mattel have utilized Spatial for team meetings, product design sessions, and virtual events, highlighting the growing adoption of Metaverse technologies in corporate settings.Why is Crypto so Important in the Metaverse?
Generally, decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols play a vital role in the Metaverse by providing financial infrastructure for borrowing, lending, and earning interest on digital assets. Platforms like Aave and Compound enable users to leverage their cryptocurrency holdings as collateral to borrow funds or earn passive income through yield farming and liquidity provision. These DeFi services enhance the financial ecosystem of the Metaverse, offering users additional ways to interact with their digital assets and participate in decentralized finance activities.What Role does VR Play in the Metaverse?
What will the Metaverse be Used for in the Future?
Shopping in the Metaverse
Gaming in the Metaverse
Healthcare in the Metaverse
Education in the Metaverse
Are Web3 and Metaverse the Same Thing?
Top Metaverse Companies

Advantages and Disadvantages of the Metaverse
Advantages
Disadvantages
Metaverse Pros and Cons
How Will the Metaverse Change My Life?
Conclusion – Is the Metaverse Here to Stay?
Metaverse FAQs
What is the Metaverse in simple terms?
What is the purpose of Metaverse?
Can anyone access the Metaverse?
How do I get into the Metaverse?
Is the Metaverse free?
Is Mark Zuckerberg the owner of Metaverse?
Who owns the Metaverse?
Does the Metaverse still exist?
How many Metaverses are there?
References






 Kane Pepi
Kane Pepi 


 Nick Pappas
Nick Pappas