Bitcoin Transaction Fee Estimators: What Are They and How Do You Use Them
Whenever there’s a bitcoin (BTC) rally, bitcoin transaction fees tend to go up. If you want to know what current Bitcoin network fees are, you can take a look at bitcoin transaction fee estimators.

In this article, we will delve into what they are, what they do, the challenges they face, and how you can use them in an efficient manner.
What are Bitcoin transaction fee estimators?
Bitcoin fee estimators are an important part of the Bitcoin ecosystem for casual and experienced users alike because they help users navigate the dynamic fee ecosystem designed by Bitcoin’s pseudonymous creator, Satoshi Nakamoto.
Each block in the Bitcoin blockchain is composed of a set of transactions. However, each block must be less than or equal to 1MB (1,000,000 bytes). Additionally, the Bitcoin network is designed such that each block should be mined every ten minutes, on average. As a result of the restricted size of each block, there are a limited number of transactions that can be included per set.
Bitcoin miners are incentivized to add transactions with the highest processing fees in order to maximize their fee earnings. For users, this presents a dynamic situation where they are likely to pay more or less depending on the network demand at the time.
When many people are using the network, there is high demand and, as such, miners will pick the transactions with the highest fees to get added to the block first. This, in turn, creates a sort of bidding war amongst users who will add high fees to their transactions in order to maximize the chances of their payments getting the first block confirmation quicker.
Conversely, when demand is lower, you are more likely to get a transaction with smaller fees added to a block quicker. Since Bitcoin network usage fluctuates, sometimes wildly, it can be challenging to approximate the right fee to add to a transaction.
This is what bitcoin transaction fee estimators help users do.
Things to consider
Due to the dynamic nature of the network fee, BTC fee estimators can only approximate the amount you should add to your transaction as a fee based on current network statistics. However, the network is likely to have fluctuated when you transfer your funds.
The inaccuracy of BTC fee estimators is a common complaint among BTC users, with many decrying the inefficiency of the tools available on the market.
The transaction fee only affects the amount of time you will need to wait until your transaction gets the first confirmation. After the first confirmation, which is affected by factors explained earlier, parties require between 2 or 6 confirmations to accept the transactions valued.
The time users wait for the additional rounds of confirmation is not affected in any way by the fee initially attached to the transaction. The network is designed to have a block every ten or so minutes.
It is possible to see transactions with low fees in the mempool during times of high demand. This is typical because of a technique called Child-Pays-For-Parent (CPFP).
CPFP allows users to reprioritize low fee transactions because a high fee transaction depends on its confirmation. Its name is a reference to the fact that the newer transaction depends on the older one.
Another technique you may see is the “Replace-By-Fee” (RBF) approach. Using this technique, users reserved the option to change the fee after the transaction is broadcast and registered in the mempool, where all the valid transactions wait to be confirmed. If the fee on his transfer is too low, the user can increase it to make it more attractive for the miners.
How to use Bitcoin fee estimators
There are a number of BTC fee estimators currently available on the market. Examples include Txstats and Statoshi. It is important to note that you don’t have to use fee estimators when sending a BTC transaction. You can simply add a high fee for ensured confirmation or low ball it and leave it to chance.
However, if you do decide to streamline your transfer, the first step is to use a fee estimator to study the mempool. By looking at the number of unconfirmed transfers waiting in the mempool, it is possible to gauge the demand on the network and thus the average amounts the miners are looking to get per transaction.
A favorite among bitcoin users is Johoe’s Bitcoin Mempool Statistics because of its collection of comprehensive graphs that help shed light on the state of the Bitcoin mempool and its effect on the fees. However, its layout may prove too complex for the new user.
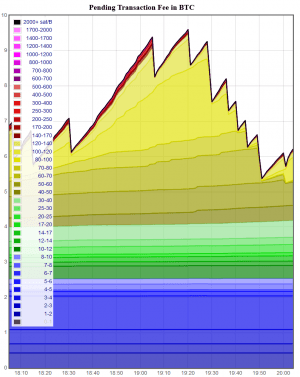
Another well-used resource is Mempool.space. With its easier-to-grasp graphs, even the novice BTC user is likely to find it easily navigable.
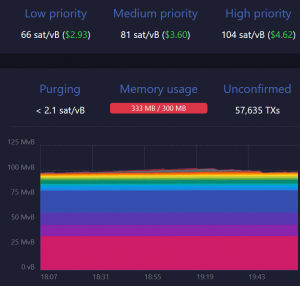
Once you have used any of the fee estimators, you will still need to manually set your BTC fees. The key is to set it higher than the average fee miners are accepting at that point. If your transaction is urgent then you can set a much higher than the average fee to effectively guarantee its faster confirmation.
Finally, while it is important to know how to do all this for yourself manually, there are convenient tools that automate the fee process for you. Some examples are those wallets that have enabled R-B-F such as Wasabi, Trezor, and Electrum.
___
Learn more:
Bitcoin Users Could’ve Saved Half a Billion USD in Fees – Report
How to Use Bitcoin SegWit Transactions: a Guide
Here is the Best Time of Day to Save on Ethereum Gas Prices




